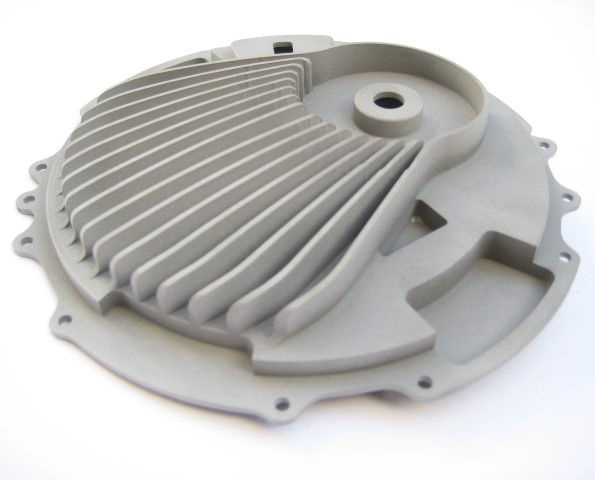
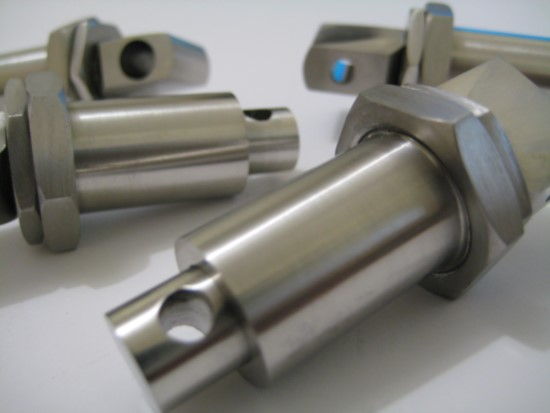
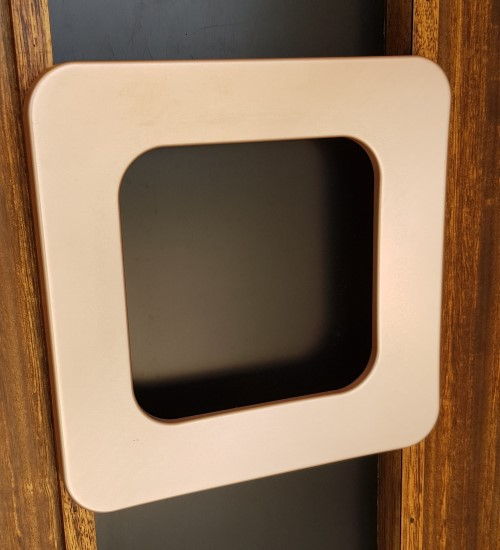
Setup cost is higher
In CNC machining process, initial setup cost is higher, it's not as simple as printing on 3D printer.
Firstly, you need to use CAM program to prepare the machine code (also known as NC code), which is used to control, automate, and monitor the movements of a CNC machine.
However, once you have a NC code prepared, it can be used again and again to produce identical parts.
Sometimes rigid and purpose built work-holding devices required, depends upon the part geometry.
Hollow parts are hard to machine
Contrary to 3D printing, it's difficult to machine voids or hollow parts. If it's necessary, then parts need
to be cut into sections and bonded after machining the internal voids. The undercuts are also challenging to machine.
Human intervention
The machine operator has a significant level of control over the accuracy of a CNC machining project. Careful
attention is required from the machine operator to ensure that all the product features are machined to the full extent.